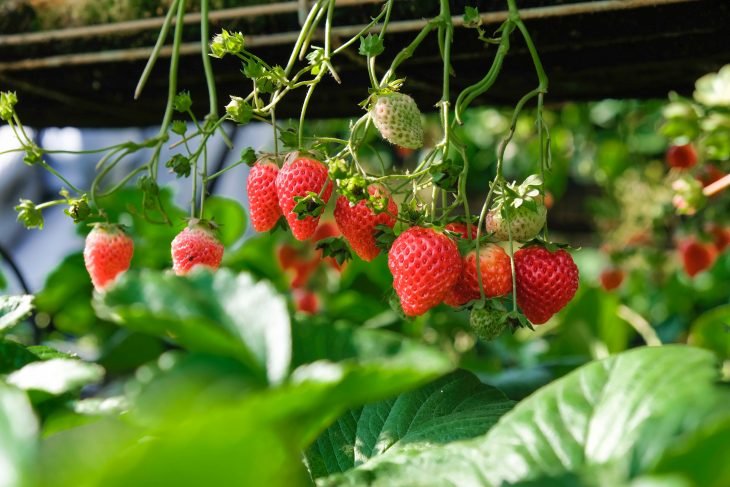
Strawberries are among the most loved fruits worldwide, known for their sweetness, fragrance, and versatility in desserts, smoothies, and snacks. Traditionally, strawberries have been grown outdoors in soil, which requires plenty of space, water, and attention. But in recent years, a new and highly efficient growing method has gained popularity: hydroponic strawberries.
This modern approach to farming eliminates the need for soil, conserves resources, and can produce fresh strawberries year-roundeven in areas where traditional farming is almost impossible. If youve ever wondered what are hydroponic strawberries or how a plant grows without soil, this article will give you a detailed answer.
Well also explore the advantages, challenges, best systems, and care tips for hydroponic strawberry plants to help gardeners, farmers, and entrepreneurs who are considering this innovative method of cultivation.
What Are Hydroponic Strawberries?
Hydroponic strawberries are strawberries grown in a soil-free system where plants receive nutrition through a water-based, nutrient-rich solution. Instead of relying on soil to deliver essential minerals, hydroponics uses carefully balanced formulas that provide nitrogen, potassium, magnesium, calcium, and other nutrients directly to the roots.
In hydroponics, the roots are supported by an inert growing medium such as coconut coir, perlite, rockwool, or clay pebbles. These mediums do not supply nutrients themselves but provide structure and aeration so the plants can grow optimally.
Hydroponic strawberries are gaining attention because they allow farmers to produce berries in controlled environments like greenhouses or vertical farms. This means fresh fruits can be made available year-round without depending on weather or geography.
How Do Hydroponic Strawberry Plants Grow Without Soil?
The concept might sound unusual at firstafter all, we usually associate gardening with soilbut hydroponic strawberry plants thrive because all the crucial growth factors are carefully provided in a soil-free environment.
Heres how the growth process works step by step:
-
Seedlings or Runners: Growers start with young strawberry seedlings or runners, just as they would in soil-based farming.
-
Planting in a Hydroponic Medium: Instead of planting into soil, the seedlings are placed in a growing medium like coconut coir or clay pellets.
-
Nutrient Delivery: An aqueous solution enriched with essential nutrients flows directly to the root zone. This liquid replaces what the plant would otherwise extract from soil.
-
Controlled Lighting and Climate: In many hydroponic setups, growers regulate temperature, humidity, and light (either through greenhouses or LED systems). This control allows strawberries to grow faster and healthier.
-
Pollination: Since strawberries typically rely on insects and wind for pollination outdoors, indoor hydroponic strawberries are hand-pollinated or use fans and bumblebees within greenhouses.
-
Harvesting: Within 810 weeks of planting, strawberries are ready for harvest. Theyre often sweeter and more uniform than soil-grown ones due to the balanced nutrient conditions.
Benefits of Growing Hydroponic Strawberries
There are several reasons why growers are turning to hydroponic strawberry systems instead of traditional soil farming.
-
Year-Round Production: Hydroponics allows you to grow strawberries in any season, regardless of outdoor weather.
-
Space Efficiency: Vertical farming methods maximize small spaces, perfect for urban farming.
-
Cleaner Fruit: Since strawberries dont touch the soil, they are cleaner, requiring less washing before consumption.
-
Water Conservation: Hydroponic systems recycle water and use up to 90% less water than traditional farming.
-
Higher Yields: Plants grow faster and more consistently because they receive exactly what they need.
-
Reduced Pest Problems: Soil-borne pests and diseases are eliminated, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
In fact, many large-scale farming operations worldwide have already shifted major production to hydroponics due to these advantages.
Types of Strawberry Hydroponic Systems
When it comes to cultivating hydroponic strawberries, choosing the right system is critical. Different hydroponic setups impact yield, maintenance, and cost. Here are the most commonly used methods:
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
This popular system continuously flows a thin film of nutrient water across the plants roots in sloped channels. Its perfect for strawberries since the shallow roots thrive in this constant nutrient stream.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Plants are suspended in a tank with their roots submerged directly into nutrient-rich water. For strawberries, this works best with added support to prevent crown rot.
Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain)
In this method, the container is periodically flooded with nutrients and then drained to provide oxygenation. This technique mimics natural cycles and supports healthy root growth.
Drip Irrigation System
A frequent choice for larger strawberry farms, this system delivers nutrients through drip emitters placed near each plant. Its efficient and easy to customize.
Vertical Hydroponic Towers
These are space-saving solutions where strawberry plants grow in stacked towers. Perfect for commercial growers or urban gardens, they maximize yield with minimal space.
Are Hydroponic Strawberries Organic?
One question people often ask is whether hydroponic strawberries are organic. The answer depends on certification rules in different regions. In the United States, for example, hydroponic crops can sometimes be labeled organic if they meet USDA guidelineseven without soil.
However, traditional organic farming purists argue that true organics require soil. Regardless of certification, hydroponic strawberries are often healthier and safer because they minimize pesticide use.
Taste and Quality of Hydroponic Strawberries
Many consumers are pleasantly surprised by the flavor of strawberries grown hydroponically. Because growers carefully control nutrient supply and environment, the berries often come out sweeter, juicier, and more visually attractive than mass-produced field strawberries.
In blind taste tests, hydroponic strawberries often rank equally highor even higherthan soil-grown berries. Since conditions are optimized, the fruits develop uniform ripeness and fewer deformities.
Common Challenges in Hydroponic Strawberry Farming
While hydroponic systems have numerous benefits, growers can face challenges such as:
-
High Initial Costs: Setting up a complete hydroponic greenhouse or tower system requires significant investment.
-
Technical Knowledge: Farmers must manage nutrient formulas, lighting, and pH levels carefully.
-
Pollination Needs: Since natural pollinators are scarce indoors, growers must invest time in pollination techniques.
-
Temperature Sensitivity: Strawberries like cooler temperatures (6080°F), so environmental control is essential, especially in warmer climates.
Proper research and planning can offset these challenges. Many agricultural institutions and resources such as University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources provide detailed guides and studies for aspiring hydroponic strawberry growers.
Growing Hydroponic Strawberries at Home
Hydroponics isnt only for large farmsit can also be done at home. With the availability of small-scale strawberry hydroponic systems, even hobbyists can grow fresh strawberries on balconies or indoors.
To start at home:
-
Select a small hydroponic system kit (NFT or vertical systems are best for strawberries).
-
Buy disease-free strawberry seedlings or bare-root runners.
-
Use a nutrient mix tailored for fruiting plants.
-
Maintain pH at 5.86.5 for optimal results.
-
Ensure proper light exposure (at least 1214 hours a day with LED grow lights indoors).
-
Hand-pollinate flowers using a small brush to ensure fruiting.
With patience and consistency, home growers can enjoy fresh, pesticide-free strawberries throughout the year.
The Future of Hydroponic Strawberry Farming
With the global population growing and farmland decreasing, hydroponics holds immense promise for the future. Cultivating hydroponic strawberries not only ensures local, sustainable, and eco-friendly fruit production but also reduces dependence on imports from soil-based farms.
Vertical farms in urban areas are already cutting down food miles and providing fresher produce to city residents. With technological advancements like AI-driven nutrient monitoring and automated irrigation systems, we can expect hydroponics to become mainstreameven for strawberries.
Read More: How to Build a Hydroponic Strawberry System at Home
Final Thoughts
So, what are hydroponic strawberries? They are the future of sustainable horticulturefruits grown without soil, nurtured with precision, and harvested with care. Whether cultivated in commercial greenhouses or home setups, hydroponic strawberry plants provide an innovative solution to modern agricultural challenges.
By adopting a strawberry hydroponic system, growers can produce higher yields, save resources, and supply fresher fruits year-round. And for consumers, it means sweeter, healthier strawberries on the table regardless of season or geography.
Hydroponic strawberries are more than just a farming trendthey are a step toward sustainable food security in an ever-changing world.